Evaluation of the psychometric properties and clinical applications of the Timed Up and Go test in Parkinson disease: a systematic review
Article information
Abstract
To review and systematically summarize the psychometric and clinical properties (reliability, validity, responsiveness) of the Timed Up and Go test applied to persons diagnosed with Parkinson disease. A systematic review was performed by screening four scientific databases (MED-LINE, CINAHL, and PubMed). Independent reviewers selected and extracted data from articles that assessed the reliability, validity, sensitivity to change, and/or clinical properties of the Timed Up and Go test in persons with Parkinson disease. Twenty-four studies were selected. Nine analyzed reliability and yielded “good” to “moderate” scores. Seventeen used a range of different contrast tests to assess validity of the Timed Up and Go test and found “good” quality scores in those that assessed balance. Only two studies analyzed sensitivity to change and they reported “poor” quality scores. The use of Timed Up and Go in Parkinson disease patients presents good reliability and validity (when compared to tests that assess balance).
INTRODUCTION
Parkinson disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disease associated with the degeneration of dopamine-producing cells in the substantia nigra (Zhang et al., 1999). Persons with PD are known to have a forward-leaning posture, an unsteady gait, difficulty in initiating movements, marked postural instability, bradykinesia, masked facial expression, and tremor (Mera et al., 2012). Horak et al. (1992) and colleagues described the difficulty experienced by these persons for sequencing and implementing posture correction strategies. These movement disorders are characteristic to PD and can seriously compromise functions in individuals.
Physical therapy professionals (physiotherapists, rehabilitation doctors, etc.) teach PD patients strategies to deal with such disabilities, facilitating their easy movement, minimizing disability, and retaining independent living skills. Hence, the importance of having reliable and valid tools that can reflect their condition when performing tasks related to balance, gait, and mobility (Brusse et al., 2005).
Different tests (functional reach test, Romberg test, Sharpened Romberg Test, 6-min walk test, Functional Gait Assessment, etc.) and scales (Berg Balance Scale, Activities-specific Balance Confidence Scale, Balance Evaluation Systems Test, etc.) are currently used to assess the degree of balance and functionality of these patients, and the Timed Up and Go (TUG) test is the most frequently used one (Palmerini et al., 2013).
The TUG test was created and validated by Podsiadlo and Richardson (1991) to assess dynamic balance, mobility, and the risk of falls in older persons, through the modification of the “Get Up and Go” test (Mathias et al., 1986). Both tests assess mobility in older adults, where tasks consist of getting up from a chair, walking 3 m, turning around, returning to the chair and sitting down. However, in the Get Up and Go test, time is not measured but a video is recorded and mobility is classified on a scale from 1 to 5, where 1 is “normal” and 5 is “severely abnormal”. Podsiadlo and Richardson (1991) incorporated a time component to increase measurement reliability but they ensured that the test continued to be quick and easy to manage. This parameter was assessed in a sample population aged 60–90 years and gave an intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) reliability score of 0.99 for both interevaluator and intraevaluator. In terms of validity, TUG times were moderately correlated with walking speed scores in the Berg Balance Scale and the Barthel Activities of Daily Living Index.
Even though the TUG is currently known to be a highly reliable and valid tool for assessing older populations, little is known of its psychometric and clinical properties (reliability, validity, responsiveness) in PD patients despite being widely used with such populations. Hence the need to perform this study, whose main objective is to systematically review and summarize the clinical properties (reliability, validity, responsiveness) of the TUG test applied in PD patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The method used in this project has been reported in detail in prior reviews of other domains (Tyson et al., 2008; Tyson and Connell, 2009a, 2009b) and has been reproduced here but by introducing aspects specific to reviewing walking and mobility measurements.
Search strategy
A comprehensive search of PubMed, MEDLINE, and CINAHL databases was performed to identify the relevant publications from 1991 to January 2019. These databases were chosen because they cover a variety of disciplines and integrate information from the fields of biomedical clinical practice and health. Moreover, the authors’ personal libraries were manually searched for further publications. The databases were searched using the following index terms and keywords or their synonyms: “Parkinson Disease” OR “PD”, “Timed Up and Go” OR “Time Up and Go” OR “TUG” “Psychometric Properties” OR “Psychometrics,” “Reliability” AND “Responsiveness” OR “Sensitivity”. Bibliographies of key articles were hand searched to ensure that relevant articles were not missed. Two reviewers (01 and 02) examined the titles and abstracts of the retrieved articles following the inclusion criteria. Findings were discussed regularly, and a third reviewer (03) was consulted in case of disagreement. A validated search filter was used to search studies on measurement properties (Terwee et al., 2009).
Inclusion criteria
Publications were included if they met the following criteria:
Patients with PD.
Design of research was cross sectional, longitudinal or descriptive and examined the psychometric properties, including reliability, validity, and sensitivity to change of the TUG test.
Studies were published between 1991 (date on which the original article by Podsiadlo and Richardson was published) and January 2019.
Language of publication was English, Spanish, or Portuguese.
Data extraction
Two independent reviewers (01 and 02) initially screened the study titles and abstracts for eligibility, after which they examined and evaluated the full texts of all relevant articles. Disagreements were resolved through consultation with a third reviewer (03). The pair of review authors then extracted data independently, and any disagreement was resolved by consensus or consultation with a third reviewer (03). The following information was extracted from the articles reviewed: age, sample size, type of design, Hoehn and Yahr stage, test used, distance, testing periods, and information on validity, reliability, and responsiveness.
Quality assessment of the study methodology and measurement properties
Data on psychometric properties and clinical utility of the measurements were then extracted from the selected articles by two independent reviewers (01 and 02) from University of Vigo, using standardized instructions and data extraction forms (Tyson and Connell, 2009a, 2009b; Tyson et al., 2008). Any disagreement was resolved through consensus or consultation with a third reviewer (03). The psychometric properties assessed are shown in detail in Table 1. A measurement tool should obtain “good” scores for reliability, validity, and sensitivity prior to its recommendation for use in clinical practice.
RESULTS
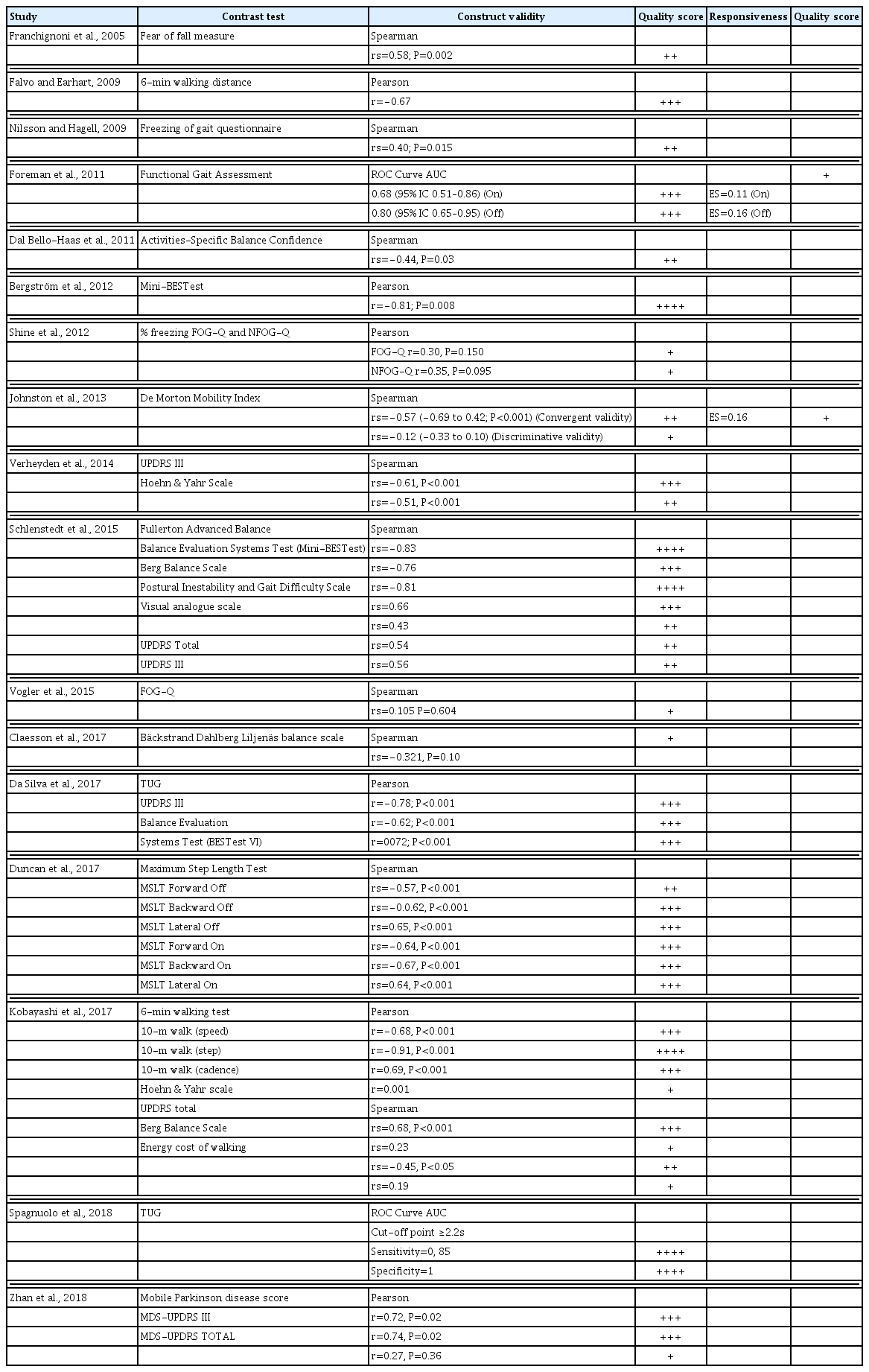
An initial search identified 179 studies relevant to the purpose of this review. The titles and abstracts were screened using the inclusion criteria and 46 studies were selected. After reading the full text of these articles, 24 studies met the inclusion criteria and were included in the review (Bergström et al., 2012; Claesson et al., 2017; Da Silva et al., 2017; Dal Bello-Haas et al., 2011; Duncan et al., 2017; Falvo and Earhart, 2009; Foreman et al., 2011; Franchignoni et al., 2005; Huang et al., 2011; Johnston et al., 2013; Kleiner et al., 2018; Kobayashi et al., 2017; Lim et al., 2005; Mariani et al., 2013; Morris et al., 2001; Nilsson and Hagell, 2009; Schlenstedt et al,. 2015; Shine et al., 2012; Spagnuolo et al., 2018; Van Lummel et al., 2016; Verheyden et al., 2014; Vogler et al., 2015; Zhan et al., 2018). The selection procedure is summarized in Fig. 1. A meta-analysis could not be performed because the TUG test was contrasted using very diverse variables, and hence results are presented in a narrative manner divided into the following sections: characteristics of the studies, testing protocol, reliability, measurement errors, validity, and responsiveness. Descriptions of the characteristics of the studies, including clinical characteristics of the TUG test, are presented in Table 2. Table 3 shows studies that carried out a TUG reliability analysis, the coefficients used and the quality score obtained. Table 4 shows the analysis of validity and responsiveness, as well as a quality score for both parameters.
Characteristics of the studies
Twenty-four articles (published in English between 2005 and 2018) that studied the psychometrics of the TUG test were included in this review. The total number of patients reviewed was 939, and of these, Johnston et al. (2013), had the most at 102 patients, while Bergström et al. (2012), had the least at just 9. In terms of gender, there was a prevalence of males (66%), but all studies contained both men and women, save in the case of Bergström et al. (2012), Shine et al. (2012), and Johnston et al. (2013), which do not differentiate by gender. All 24 articles reviewed included persons clinically diagnosed with PD, except in the case of Salarian et al. (2010) and Mariani et al. (2013), which had PD patients and a control group composed of healthy subjects with no PD. However, they only analysed PD patients’ data. The average age of patients was 66.75 (3.23) years, and the age interval ranged from 37 to 83 years. The stage of Hoehn and Yahr (1967) was recorded inconsistently in the different studies where some papers published range, while others published the number of people in each stage, and still others expressed stage through mean and standard deviation. It is also important to note that some authors used the traditional Hoehn and Yahr scale (stages 1 to 5), while others used the modified scale with intermediate stages (1.5, 2.5, 3.5, 4.5). Morris et al. (2001), not report the stage in PD patients. The sample studied in this review presents a range from I to IV, the most prevalent being stage II. Insofar as the time of assessment is concerned, only Nilsson and Hagell (2009) collected data in both the “On” and “Off” states of the subjects, while data collection in the other studies was only done in the “On” state. Foreman et al. (2011) do not provide a description of the on/off state of the patient, but they do perform a division when analysing validity and responsiveness. In terms of study design, all of them show a cross sectional design except for the study by Johnston et al. (2013), which is a prospective cohort study. Table 2 shows the test performed, testing period and the distance variations, which will be addressed in the next section.
Testing protocol
Most studies included in our review explicitly describe how the TUG test is carried out save for a few that do not explain what the test is about but refer to the study of Podsiadlo and Richardson (1991) which provides step-by-step details on how to perform the TUG test. It should be noted that the study of Salarian et al. (2010) used a distance of 7 m, that of Shine et al. (2012) used 5 m, while the remaining studies reviewed used the standard distance. Moreover, most studies conducted the (pre-post) tests on the same day, but Dal Bello-Haas et al. (2011) conducted them after 12.9 and 5.1 days respectively, and Verheyden et al. (2014) after 8 days. And lastly, it should be noted that there are other nomenclatures used for the TUG as in the case of Lim et al. (2005), who call it Timed Get Up and Go test. Technological tools were also used to implement the TUG test and these tests are referred to as inertial Timed Up and Go (iTUG) and assessment of biomechanical strategies-TUG, as in Salarian et al. (2010), Shine et al. (2012), and Da Silva et al. (2017). In order to perform the iTUG, Salarian et al. (2010) used 7 inertial sensors (accelerometer and gyroscope) connected to each other and placed on the forearms, thighs, legs, and sternum, while Shine et al. (2012) recorded a video of the test performed on a taped box, instead of a cone, like in Da Silva et al. (2017), who also used a video camera.
Reliability
Reliability, in simple terms, describes the degree of consistency of a measure. A test is reliable when it yields the same repeated result under the same conditions. Of the 23 studies selected only 10 recorded reliability and the data are shown in Table 3. Reliability was assessed using the following three procedures: (a) test-retest reliability (ICC), (b) Intrarater reliability (ICC and kappa index), which is the degree of agreement among repeated administrations of a diagnostic test performed by a single rater, and (c) interrater reliability (ICC), which is the degree of agreement among raters. It is a score of the degree of homogeneity or consensus that exists in the ratings given by various judges. The studies recorded ICC values within the 0.69–0.99 range, which is equivalent to “moderate” (0.6–0.8) and “good” (>0.8) quality scores, regardless of the reliability procedure used. Morris et al. (2001), Verheyden et al. (2014), Da Silva et al. (2017), Lim et al. (2005), and Van Lummel et al. (2016) obtained the best ICC, where the range lay between 0.85 and 1.00, which is equivalent to a “good” (>0.8) quality score.
Standard error of measurement
The standard error of measurement (SEM) is a measure of the extent to which measured test scores are spread around a “true” score. The SEM is especially meaningful to a test taker because it applies to a single score and uses the same units as the test. The SEM and reliability are related but different concepts. The SEM is a function of both the standard deviation of observed scores and the reliability of the test. When the test is perfectly reliable, the SEM equals 0. The SEM was analysed in studies undertaken by Dal Bello-Haas et al. (2011), Huang et al. (2011), and Lim et al. (2005), who obtained values between 0.59 and 3.43, depending on the development protocols used to calculate TUG measurement reliability.
Validity
In psychometrics, validity has a particular application known as test validity: “the degree to which evidence and theory support the interpretations of test scores” (“as entailed by proposed uses of tests”). The validity of TUG was assessed in 17 studies. Construct validity was assessed using the Pearson and/or Spearman correlation coefficients, but Foreman et al. (2011) and Spagnuolo et al. (2018) used receiver operating characteristics plots and area under the curve. Several tests were used to check the validity of the TUG test. The contrast tests worth highlighting are balance tests such as Mini-BestTest or Berg Balance Scale, walking tests such as the Functional Gait Assessment or 6-min walk test, Blockage tests such as the Freezing of Gait Questionnaire. Contrast was also performed by using stages and questionnaires such as the Hoehn and Yahr stage/scale and the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS). The predominant quality scores recorded were “moderate” (0.6 to 0.8) and “good” (>0.8). Also recorded, but to a lesser extent, were “poor” (<0.4) and “weak” (0.4–0.6) scores. The results are shown in Table 4.
Responsiveness
A review of the literature suggests that there are two major responsiveness aspects. We define the first as “internal responsiveness,” which characterises the ability of a measure to change over a prespecified time frame, and the second as “external responsiveness” which reflects the extent to which changes in a measure relate to the corresponding changes in a reference clinical or health state measure. The properties and interpretation of the commonly used internal and external responsiveness statistics were examined. Of the 23 studies included in this review, only two calculated responsiveness in the TUG test, i.e., Foreman et al. (2011) and Johnston et al. (2013) where scores ranged from 0.11 to 0.16, which is equivalent to a “poor” (<0.4) quality score in both studies. Mention must be made that Foreman et al. (2011) observed responsiveness both in the “on” and “off” states.
DISCUSSION
Twenty-three studies were evaluated from the descriptive and methodological quality points of view (validity, reliability, standard error measurement, and responsiveness) following criteria set out in Table 1.
The descriptive analysis revealed that sample size is conditioned by the type of analysis performed in the study. The study carried out by Bergström et al. (2012), includes a significantly low number of persons diagnosed with PD (n=9), hence the results obtained can by no means be generalized. On the other hand, 10 studies present a sample of 20–29 subjects, and 11 studies of 30–85 subjects, which is a big enough study sample for this neurodegenerative pathology. The average age of the sample was 66.75 years and ages ranged from 37 to 83 years. This age variation indicates that we should be cautious when comparing data from different studies (inter/intra study) because older persons, whether or not suffering from this pathology, undergo physical and cognitive deterioration as they age, which affects their balance and strength capacities. Hence, older persons should not be compared with younger ones, even though both types suffer from PD. Therefore, subsequent studies that analyse these psychometric properties should differentiate the sample according to their age groups. Insofar as gender of sample is concerned, the articles did not analyse results based on sex, so perhaps there may be no influence of gender on the results (Tyson and Connell, 2009a, 2009b). The sample presented Hoehn and Yahr (1967) stages I–IV, but only a descriptive analysis of the stages was performed, without breakdown by psychometric properties or stages presented by subjects. We believe that the sample should be divided into stages when performing these analyses rather than just providing a descriptive data of the population. This is because balance is only affected from stage 2.5 onwards and not in all stages of the disease. Unlike the original Hoehn and Yahr scale, the current one has substages, which limits inter study comparison (Hoehn, 1992). This qualitative pathological assessment tool should provide not only measures of central tendency and standard deviations but also percentage results.
One characteristic of patients diagnosed with PD is that they can have “off” states/episodes (In the “off” state, disease symptoms reappear with an altered motor function, while in the “on” state there is satisfactory control of symptoms with possible normal motor activity), and therefore the relevance of always recording patient’s state (on/off) so that assessment is always done under the same conditions, with high test reliability.
On the subject of protocols for carrying out the TUG test, please note that all articles analysed refer to the study of Podsiadlo and Richardson (1991), wherein the TUG is carried out over a distance of 3 m between the chair and the cone. By contrast, Salarian et al. (2010) and Shine et al. (2012) include distances of 7 and 5 m respectively, but no proper justification is provided in their papers. The iTUG used by Salarian et al. (2010) is a cell phone application that was created for 3- and 10-m distances, but was reduced to 7 m due to space constraints to perform the assessment. Shine et al. (2012), on the other hand, carried out a modified TUG, by placing a taped box instead of a cone at a distance of 5 m from the chair. In this test, the subject has to perform four different sequences: walk around the taped box, move along its edge, walk one and half times the distance, and around the chair before sitting down. Thus, we can see that there are modifications and variations to the TUG, both in terms of distance travelled and the turns performed, which is why we must be cautious when comparing results and check whether the standard TUG or any modification of it was used.
The TUG test (Podsiadlo and Richardson, 1991) is performed by clocking time manually, but the use of technologies and software (mobile application, inertial sensors, video recording system, iTUG device) developed to perform this test has now improved its reliability. Test-retest, intrarater, and interrater reliability are “good” at ranges of 0.90–0.97, 0.80–0.99, and 0.95–0.99, respectively. Our observations suggest that the use of technological tools provides reliable results in Parkinsonian samples. One of the many innovative tools that can be used in the TUG for assessing dynamic balance in PD patients is the Wiva sensor (Mollinedo-Cardalda et al., 2018). Hence, it would be interesting to use technological tools to conduct TUG assessments, with a view to identifying new more sensitive parameters for evaluating dynamic balance in persons diagnosed with PD.
The remaining studies that analyzed TUG reliability (Dal Bello-Haas et al., 2011; Huang et al., 2011; Lim et al., 2005; Mariani et al., 2013; Morris et al., 2001; Verheyden et al., 2014) without using technological tools also showed some “good” (Brusse et al., 2005; Dal Bello-Haas et al., 2011; Huang et al., 2011) and “moderate” (Dal Bello-Haas et al., 2011; Mariani et al., 2013; Steffen and Seney, 2008) scores for test-retest. Results were “good” for the intrarater and interrater (Lim et al., 2005; Verheyden et al., 2014) just like in the case of studies that used different software. Therefore, our observation indicates that technologies do not influence these parameters. Only three studies (Dal Bello-Haas et al., 2011; Huang et al., 2011; Lim et al., 2005) analyzed SEM without using technological aids in TUG. They presented high and dissimilar SEM values. More research is needed into analysis of this parameter and its relationship to the use of technological tools.
The most recorded psychometric property was validity of the TUG (in 17 studies) for which a wide variety of contrast tests were used. We, therefore, structured the TUG validity analysis as a function of the quality or the physical capacity evaluated as contrast in these studies. With regard to the contrast test for balance, the scores shown are “good” for the Mini-BESTest (Bergström et al., 2012), Berg Balance Scale and Fullerton Advance Balance (Schlenstedt et al., 2015); “moderate” for the Mini-BESTest (Da Silva et al., 2017; Schlenstedt et al., 2015) and Maximum Step Length Test (Duncan et al., 2017); “weak” for the Berg Balance Scale (Kobayashi et al., 2017) and Fear of Fall Measurement (Franchignoni et al., 2005); and “poor” for the Bäckstrand Dahlberg Liljenäs balance scale (Claesson et al., 2017). The TUG test gave different results when contrasted with the same test that assessed balance. This was the case of the Berg Balance Scale, where Schlenstedt et al. (2015) obtained a score of “good”, while Kobayashi et al. (2017), got a “weak” score. Contrast with the Mini-BESTest showed the same behaviour, where “good” and “moderate” scores are observed depending on the study, which is why the methodological quality of the study should be considered when interpreting the results of validity analysis. The validity of the contrast used for the TUG with respect to the tests that assess gait showed a similar behaviour to the contrast used in the balance test. We want to highlight that the TUG contrast validity analysis which used the Freezing of Gait Questionnaire, a questionnaire that evaluates freezing and blockage of gait (Nilsson and Hagell, 2009; Shine et al., 2012; Vogler et al., 2015), gave scores of “poor” and “weak,” indicating that the TUG is not the best test to determine Freezing of Gait in persons diagnosed with PD.
The UPDRS scale (describe symptomatology of patients) has also been used to analyse construct validity of the TUG, where Schlenstedt et al. (2015), observed “weak” scores while Verheyden et al. (2014), Da Silva et al. (2017), and Kobayashi et al. (2017), noted “moderate” scores. In view of the results, the TUG presents a high construct validity when we compare it with the motor dimension of the scale (UPDRS III), however, this validity is reduced when compared with the total score of the UPDRS scale. Zhan et al. (2018) used the MDS-UPDRS scale: an update of the UPDRS scale undertaken (Goetz et al., 2007; Goetz et al., 2008), obtaining the same results, with a “poor” score for the total of the test and “moderate” score for the motor part.
And lastly, the studies by Johnston et al. (2013) used the Morton Mobility Index as a contrast test, which assesses the autonomy and functionality of the subject. The scores obtained were “poor” and “weak,” which is surprising since the Morton Mobility Index is considered to be a test that evaluates dynamic balance and the degree of functionality of the subject, just like in the case of the TUG. Worth highlighting, after analyzing the different studies that deal with the validity of the TUG, is that none of them indicated the patient’s state (on/off) at the time of performing test. This information is essential for establishing validity because the states have a negative or positive impact on the results.
With regard to the psychometric responsiveness feature, only the studies of Foreman et al. (2011), and Johnston et al. (2013), reported this parameter. As can be seen in Table 4, the values of responsiveness are near to zero (0.11–0.16), i.e., they present poor sensitivity, and hence further studies are needed to substantiate the behavior of this variable due to the paucity of studies.
This systematic review performed has a number of limitations which are indicated below. The first limitation is that the articles reviewed did not analyse results stratified by gender and this in turn influences the results of the psychometric variables because the prevalence of PD is influenced by sex. Another limitation is that the Hoehn and Yahr stages are not always presented in the same way, which complicates grouping of the results. A third limitation is that only two studies include the on/off state of the patients, and we believe that this information is relevant and should be collected in the TUG test, since it influences freezing gait in persons with PD. A fourth limitation is that only two studies evaluated the psychometric properties of the test at two different moments in time, separated by more than a day, which does not permit an analysis of data stability. And finally, a multitude of different contrast tests was used for analysing validity which makes comparison between them difficult. Therefore, future research should consider the above limitations to address these methodological weaknesses. We would also recommend the inclusion of technological devices to increase data reliability.
By way of conclusion, our observation indicates that the use of the TUG test in persons diagnosed with PD presents good reliability for test-retest, intrarater, and interrater. A good validity was likewise observed in contrast tests that assessed balance.
Notes
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.